Introduction to Wind Turbine Maintenance and Efficiency
Wind turbine maintenance is an essential facet of renewable energy production, comprising various duties and responsibilities associated with ensuring the optimum condition and performance of turbines. This work sector combines technical, operational, and administrative aspects, all oriented toward maximizing wind power asset productivity while minimizing downtime. It involves an array of maintenance tasks, primarily focusing on the wind turbine’s main components such as the gearbox, generator, and turbine blades. Notably, the maintenance of offshore wind turbines requires more concerted effort due to the challenging environment they operate. Condition monitoring for early detection of component failure is employed, with maintenance management systems playing an instrumental role in coordinating the series of activities involved.
In the wind industry, one of the biggest challenges tussled with is efficient maintenance schedules’ development. With the increasing number of onshore and offshore wind farms, the cost associated with maintenance work and unscheduled stoppages is significantly high. In response, wind turbine manufacturers and wind farm operators are implementing advanced strategies like preventive and predictive maintenance to mitigate operation and maintenance (O&M) costs. The average wind speed, for instance, has a large bearing on the maintenance intervals. Also, the maintenance requirements vary between small wind turbines and larger wind turbines.
The following points provide an overview of maintenance planning:
- Systematically inspecting and carrying out maintenance work on wind turbine components.
- Optimizing the maintenance program by balancing the cost of operation and maintenance with energy output.
- Utilizing monitoring systems to control and forecast failures, extending the life of wind power capacity.
- Understanding the importance of scheduled maintenance during periods of low wind speed to maximize energy production during high wind speeds.
In conclusion, whether you’re installing a small wind turbine or managing a larger wind farm, a comprehensive maintenance strategy geared towards cost savings, high efficiency, and preventive measures can make a substantial impact on renewable energy output.
Understanding The Basics: Wind Turbine, Small Wind Turbines, And Wind Energy
 Wind energy is often hailed as a viable solution for clean energy needs, and it’s important to understand the basics before delving into more complex discussions about its implementation and maintenance. Wind turbines come in a variety of sizes: from large wind turbines generally installed at utility-scale wind farms to the smaller turbines used in residential and off-grid applications.
Wind energy is often hailed as a viable solution for clean energy needs, and it’s important to understand the basics before delving into more complex discussions about its implementation and maintenance. Wind turbines come in a variety of sizes: from large wind turbines generally installed at utility-scale wind farms to the smaller turbines used in residential and off-grid applications.
Fundamentally, all wind turbines work on the same principle: as the wind blows, it causes the physical movements of the rotor shaft, turning the wind turbine blade, and subsequently generating a substantial amount of electricity. The amount of electricity you want to generate is generally associated with the wind turbine’s size and the average annual wind speed at the installation site.
Maintaining wind power assets is essential, as any electricity can be lost if the turbines are not kept in good working order. Maintenance of wind turbines usually involves a blend of preventive and predictive measures. Wind turbines need different types of maintenance activities chalked out in a maintenance schedule, including routine inspection, servicing, and component replacements. Preventive maintenance aims to keep the wind turbine system running optimally and prevent failures.
On the other hand, predictive maintenance assists in planning for component replacement or large-scale preventive actions by analyzing data gathered from wind turbine monitoring systems to control and forecast such failures. Both maintenance costs and the cost of running the turbines are integral to the overall wind power capacity. The impact of wind on the turbines, especially high wind speeds, necessitates additional monitoring and maintenance procedures, making the maintenance costs an essential factor in the financial structuring of a wind power project.
Offshore vs Onshore Wind Turbines: A Comparative Analysis
Offshore and onshore wind turbines form an integral part of the global wind energy industry, each boasting unique advantages and challenges. Understanding the cost per unit of energy generated, the kind of maintenance required, and the overall benefits of each system can greatly assist in planning maintenance strategies and optimizing the generation of wind energy. Onshore wind turbines generally require preventative maintenance at regular intervals due to environmental factors like dust and debris. Traditionally less expensive, the cost of wind turbine installation and maintenance for onshore systems can be offset by the higher wind speeds and consistency often found offshore. However, both necessitate periodic inspections of wind turbine components that may need to be replaced or repaired.
Consider offshore wind turbines, for instance, which are often installed 30 feet above anything, thereby virtually eliminating obstruction of wind flow. These turbines are subjected to less turbulent but stronger winds, offering a great potential for wind energy. Despite these perks, preventative maintenance for offshore turbines becomes more complex, and much maintenance is carried out using specialized marine vessels or helicopters, which enhances the overall cost. Typically, offshore wind turbines used in the wind energy industry are more robust and have greater longevity, which offsets their initially higher cost.
- Preventative maintenance: Ensures wind turbines function optimally and can prolong their lifespan.
- Cost per unit of energy generated: Essential for comparing the viability of onshore and offshore wind turbines.
- Wind turbine components: Subject to regular inspection and may need to be replaced periodically to maintain performance.
- Installation and maintenance: Should be factored into the overall cost of wind turbines.
With these and other elements in mind, it is essential to remember that wind energy is one of the fastest-growing sources of electric power in the world, reducing reliance on fossil fuels instead of running turbines on non-renewable resources. Both onshore and offshore wind turbines therefore represent vital components in the progress of green, renewable energy.
A Deeper Dive into Turbine Blades: Structure and Maintenance for Optimal Energy Output
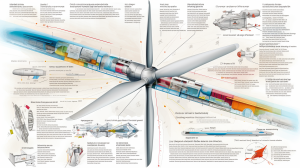 A deep understanding of the structure and maintenance of turbine blades is critical for achieving optimal energy output, particularly in the case of often-used wind turbines.
A deep understanding of the structure and maintenance of turbine blades is critical for achieving optimal energy output, particularly in the case of often-used wind turbines.
The blades of wind turbines, governed by the principles of aerofoil, play a crucial role in harnessing wind energy and transforming it into electric wind power.
This process fundamentally relies on the blade’s shape and orientation, which have a direct influence on the turbine’s energy output. Hence, the design of the blade is typically streamlined, allowing the wind to pass more quickly over one surface relative to the other, which, in turn, creates lift and propels the blade forward.
Nonetheless, this mechanical process challenges the structural integrity of the blades and necessitates regular maintenance for optimum efficiency to be sustained. The persistent exposure to harsh weather conditions results in wear and tear of the blades over time. Corrosion, blade erosion, and structural damage can reduce the output of the whole system while increasing the risk of catastrophic failures. Hence, preventative maintenance plays a pivotal role in the longevity and optimal functioning of wind turbines. This includes:
- Regular inspections for signs of damage
- Applying protective coatings to resist corrosion
- Repairing minor damages promptly before they escalate
- Regular realignment checks to ensure optimal wind exposure
Thus, the structured approach to design and routine care directly contributes to the effective and safe operation of wind turbines. With meticulous attention to blade maintenance and optimal design, wind turbines can continue to be a reliable and sustainable source of energy. This proactive approach not only maximizes energy output but also extends the lifespan of the turbines, underlining the importance of both technical design and ongoing maintenance in the realm of renewable energy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wind turbines are an integral part of our transition towards sustainable energy sources to combat climate change. These towering structures, as visually striking as they are functional, convert wind energy into electricity, often providing power to surrounding communities. The frequency of their use hinges on a variety of factors, including the strength and predictability of the wind in the area.
However, considerations must be made concerning their placement and operation, as while functional, they can pose a threat to local wildlife, specifically birds and bats. Standards and policies must be put in place to address these concerns and limit their potential environmental impact. Furthermore, while adopting wind energy on a broad scale can yield considerable benefits, it’s worth noting that wind turbines do require significant upfront investments for construction and maintenance.
In this scenario, the benefits often outdo the drawbacks, especially when we consider the long-term return on investment and the massive potential for energy production that wind turbines represent. As we continue grappling with the daunting reality of global climate change, we’ll find ourselves relying on renewable energy infrastructure like wind turbines more frequently. Despite their challenges, wind turbines are a testament to human ingenuity and our determination to harness the power of nature sustainably and responsibly.
FAQ’s:
Q1. How often do wind turbines need maintenance?
A1. Wind turbines typically require maintenance every 1-2 years in order to keep them running efficiently.
Q2. What kind of maintenance do wind turbines need?
A2. Wind turbines need regular inspections, lubrication, and cleaning of the blades and other components to ensure they are running efficiently.
Q3. What are the benefits of regular wind turbine maintenance?
A3. Regular maintenance of wind turbines can help to ensure they are running at peak efficiency, reduce downtime, and extend the life of the turbine.
Q4. What are the risks of not maintaining wind turbines?
A4. Not maintaining wind turbines can lead to decreased efficiency, increased downtime, and potential damage to the turbine.
Q5. How often should wind turbines be inspected?
A5. Wind turbines should be inspected at least once a year to ensure they are running efficiently and safely.
Q6. What should be done during a wind turbine maintenance inspection?
A6. During a wind turbine maintenance inspection, technicians should check for any signs of wear and tear, lubricate moving parts, and clean the blades and other components.
Q7. What are the most common causes of wind turbine failure?
A7. The most common causes of wind turbine failure are improper maintenance, extreme weather conditions, and mechanical failure.

Nina Jerkovic
Meet Nina Jerkovic, our expert on all things green and sustainable. With a keen eye for eco-friendly living, Nina shares practical tips and insights to help you navigate the world of sustainable choices. Join her on a mission to create a healthier planet through mindful living.


 Wind Turbine Placement and Site Assessment
Wind Turbine Placement and Site Assessment
